So readers today we are going to learn about the collection framework. Which is provided by Java. So what Collection means – any group of individual objects that are represented as a single unit. The Collection in Java is a framework that provides an architecture to store and manipulate a group of objects. It provides some predefined classes and interfaces and algorithms to the user.
The Collection interface (java.util.Collection) and Map interface (j**ava.util.Map**) are the two main “root” interfaces of Java collection classes.
So collection framework is nothing but a JAVA API.
Some advantages of using collection framework in java-
Consistent API: The API has a basic set of interfaces like Collection, Set, List, or Map, all the classes (ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, etc) that implement these interfaces have some common set of methods.
Reduces programming effort: A programmer doesn’t have to worry about the design of the Collection but rather he can focus on its best use in his program.
Increases program speed and quality: Increases performance by providing high-performance implementations of useful data structures and algorithms because in this case, the programmer need not think of the best implementation of a specific data structure.
Hierarchy of the Collection Framework
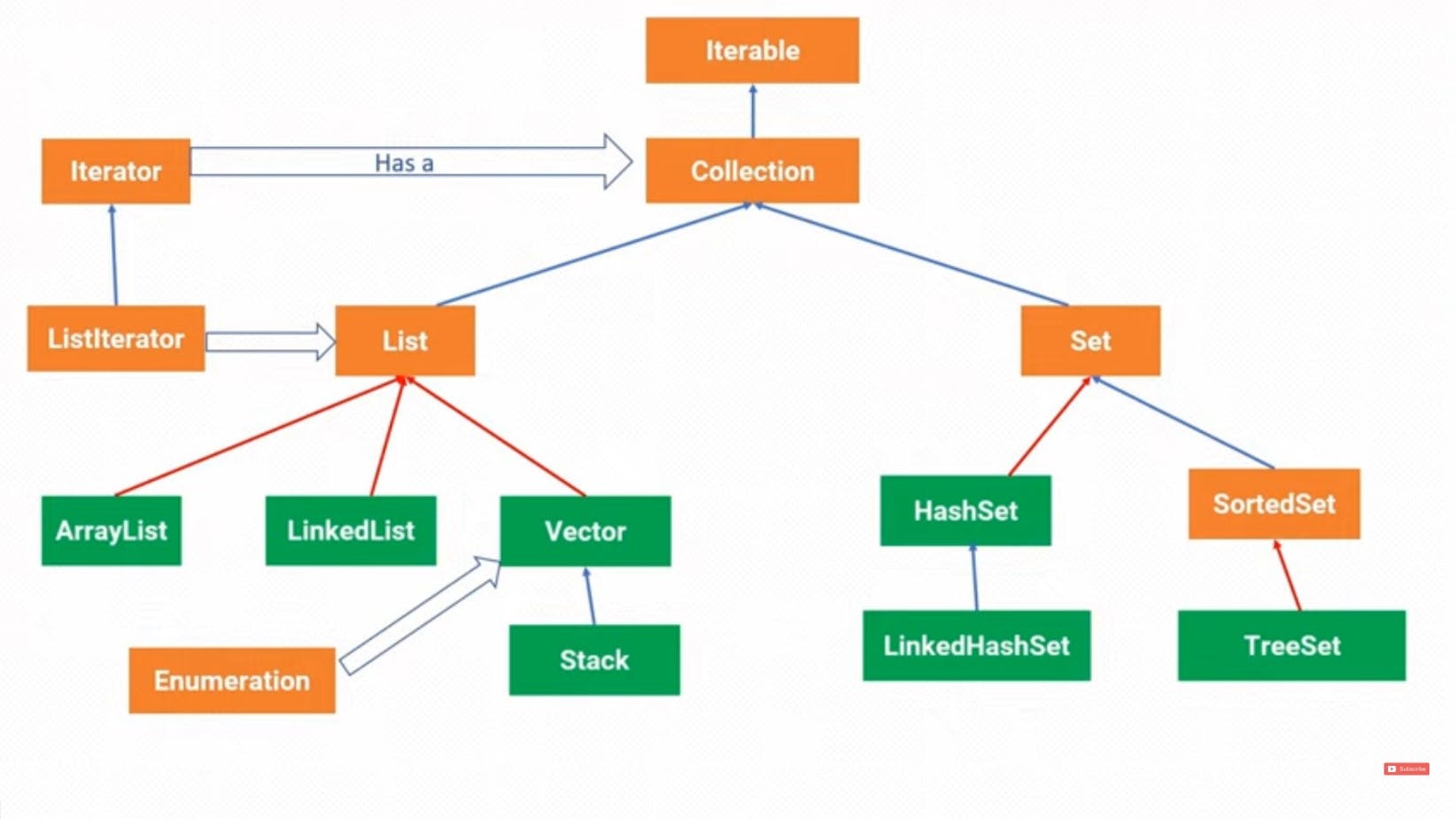
Image collected from Youtube.
The utility package, (java.util) contains all the classes and interfaces that are required by the collection framework.
Here the orange rectangles are represented as interfaces and classes are represented by green rectangles.
First, we start with the collection interface-
Collection interface:
The Collection interface is the interface that is implemented by all the classes in the collection framework. It declares the methods that every collection will have.
List interface:
The list interface is the child interface of the Collection interface. It uses a list-type data structure where we can store the ordered collection of objects. It can have duplicate values.
List interface is implemented by the classes ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, and Stack.
ArrayList:
The ArrayList class implements the List interface. It uses a dynamic array to store the elements. The elements stored in the ArrayList class can be randomly accessed.
LinkedList:
LinkedList implements the Collection interface. It uses a doubly linked list to store the elements. In LinkedList, the manipulation is fast because no shifting is required.
Vector:
Vector uses a dynamic array to store the data elements. It is similar to ArrayList. However, It is already there before the collection framework. So it contains some additional features.
It is thread-safe which means 2 threads can't use an object at the same time while ArrayList is non-thread-safe which means 2 threads can use an object simultaneously.
Stack
It is the subclass of Vector. It implements the last-in-first-out data structure. The stack contains all of the methods of Vector class.
Now we are going to discuss another child interface of the collection framework.
Set interface:
Set Interface in Java is present in java.util package. It extends the Collection interface. It represents the unordered set of elements.
It doesn't allow to store of duplicate items.
Set is implemented by HashSet, LinkedHashSet, and TreeSet.
HashSet:
HashSet class implements Set Interface. It represents the collection that uses a hash table for storage. Hashing is used to store the elements in the HashSet. It contains unique items.
LinkedHashSet:
LinkedHashSet class represents the LinkedList implementation of Set Interface. It extends the HashSet class and implements Set interface. Like HashSet, It also contains unique elements
SortedSet Interface:
SortedSet is the alternative of Set interface that provides a total ordering of its elements. The elements of the SortedSet are arranged in increasing (ascending) order.
TreeSet:
TreeSet is a class that implements the sorted set interface. It uses a tree for storage. Like HashSet, TreeSet also contains unique elements. The access and retrieval time of TreeSet is quite fast. The elements are stored in ascending order.
How we can fetch the elements:
Iterable
Iterator
ListIterator(objects are stored in a list)
Enumeration(used by vector)
We can fetch the elements or traverse the elements through some interfaces.
Iterable is extended by the collection framework by using for-each loop for traversing. It can be implemented by both List and Set interface
Iterator uses a has-a relation to fetch the elements as the collection stores the object of iterators. It can be implemented by both List and Set interface
ListIterator is an interface used by List interface and its classes, the objects are stored in a list. It is a backward method of traversing and it can't be implemented by Set interface.
Enumeration is a special interface used by vector and its class.
Readers, we will now discuss Map interface. It provides key-value pairs collections. Here duplicate keys are not allowed and order isn’t preserved.
Hierarchy of the Map interface
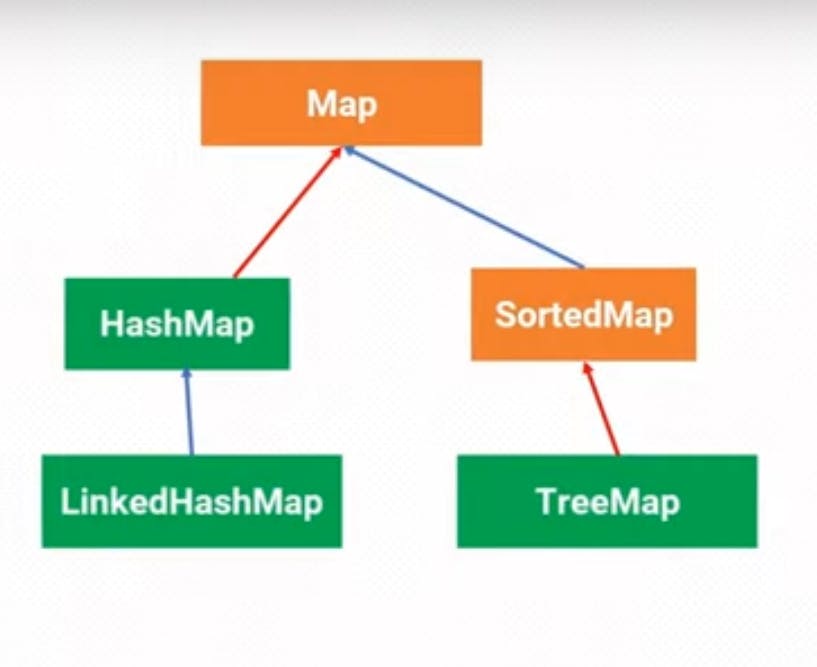
Image is collected from Youtube
So Map interface consists hashmap and sortedmap
HashMap: A class of Map,provides hash table data structure. Duplicate key values are not allowed.
LinkedHashmap : here order is preserved and duplicate keys are not allowed.
Sorted Map- Here the elements can be traversed in sorted order of keys.
TreeMap- it is a tree data structure that provides key wise sorting.
So this was the basics of collection in java. We briefly discussed the topic and hope you will understand it clearly. See you in the next blog.

