Introduction✒️
Machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Need for machine learning 📌
Nowadays, machine learning is very important because it gives organizations a view of trends in customer behavior and business operational patterns, and also it supports the development of new products. Many of today's leading companies, such as Facebook, Google and Uber, make machine learning a central part of their operations. Machine learning has become a significant competitive differentiator for many companies.
In computational language, the task environment of machine learning is: A computer program is said to learn from experience E concerning some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
Here, T means Task: Recognising and classifying handwritten words within images, P means Performance: Percent of words correctly classified, and E means Experience: A dataset of handwritten words with given classifications.
As an example, A chess learning problem where Task( T): Playing chess, Performance measure (P) is: Percent of games s/he won against opponents, Training experience (E): Practicing games against itself.
Overview 🎀
With any method, there are multiple ways to train machine learning algorithms, each having its advantages and disadvantages. To understand the benefits and limitations of each type of machine learning, we first look at what type of data they ingest. In ML, there are two types of data — labeled data and unlabeled data.
Labeled data has both the input and output parameters in a completely machine-readable pattern, but requires a lot of human labor to label the data, to begin with. Unlabeled data only have one or none of the parameters in a machine-readable form. This negates the need for human labor but requires more complex solutions.
A comparison of Unlabeled Data and Labeled data -
Unlabeled datasets are samples of natural or human-made items. Unlabeled data might include pictures, audio and video recordings, articles, tweets, medical scans, or news. These items have no labels or explanations.
While labeled datasets use human judgment to classify a piece of unlabeled data. The labels depend on the problem that needs to be resolved.
Types of Machine Learning 🪄
There are also some types of machine learning algorithms that are used in very specific use cases, but three main methods are used today.
Supervised learning
Unsupervised learning
Reinforcement learning
Supervised learning 🎉
First, we will learn about Supervised Learning, It is a type of machine learning method where we provide sample labeled data to the machine learning system to train it, and on that basis, it predicts the output. The system creates a model using labeled data to understand the datasets and learn about each data, once the training and processing are done then it is tested by providing sample data to check whether it is predicting the exact output or not. The main goal of supervised learning is to map input data with output data. It is based on supervision. An example of supervised learning is spam filtering.
Unsupervised learning 🎉
It is a learning method in which a machine learns without any supervision. The training is provided to the machine with a set of data that has not been labeled, classified, or categorized, and the algorithm needs to act on that data without any supervision. The goal of unsupervised learning is to restructure the input data into new features or a group of objects with similar patterns. In unsupervised learning, we don't have a predetermined result. The machine tries to find useful insights from a huge amount of data. It can be further classifieds into two categories of algorithms.
Reinforcement learning 🎉
It is a feedback-based learning method, where a learning agent gets a reward for each right action and gets a penalty for each wrong action. The agent learns automatically with this feedback and improves its performance. In reinforcement learning, the agent interacts with the environment and makes decisions or choices. The goal of an agent is to get the most reward points, and thus, it improves its performance. For example, self-driven cars –Reinforcement learning is used in self-driving cars for various purposes such as the following. Amazon cloud services such as DeepRacer can be used to test Reinforcement learning on physical tracks.
Trajectory optimization: Reinforcement learning can be used to train an agent for optimizing trajectories. In reinforcement learning, the software agents could get rewards from their environment after every time step by executing an action in the state.
Motion planning including lane changing, parking etc
Dynamic pathing: Reinforcement learning can be used for dynamically planning the most efficient path in a grid of potential paths.
Controller optimization.
Scenario-based learning policies for highways.
ML algorithms 📖
Machine learning algorithms are the engines of machine learning, meaning it is the algorithms that turn a data set into a model.
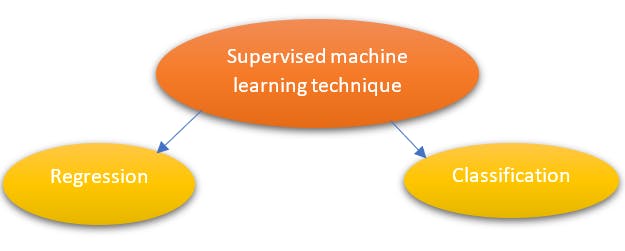
Regression:
It is a method to model the relationship between dependent (target) and independent (predictor) variables with one or more independent variables. Regression analysis helps us to understand how the value of the dependent variable is changing corresponding to an independent variable. It predicts continuous/real values such as temperature, age, salary, price, etc.
Examples of regression are Linear Regression, Polynomial Regression.
Classification:
The Classification algorithm is a Supervised Learning technique that is used to identify the category of new observations based on training data. Here, a program learns from the given dataset or observations and then classifies new observations into several classes or groups. Such as, Yes or No, 0 or 1, Spam or Not Spam etc. Classes can be called targets/labels or categories.
Examples of classification algorithms are Decision trees, Random forests,KNN trees, Naïve Bayes, and Support Vector Machines.
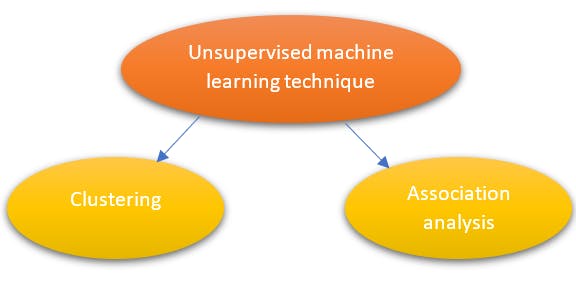
Clustering:
It is an unsupervised machine learning technique, which groups the unlabelled dataset. It is done by finding some similar patterns in the unlabelled dataset such as shape, size, color, behavior, etc., and dividing them as per the presence and absence of those similar patterns.
Example: singular value decomposition (SVD), Principal Component Analysis(PCA), K-means.
Association analysis
An association rule is an unsupervised learning method that is used for finding the relationships between variables in a large database. It determines the set of items that occurs together in the dataset.
Example: Apriori algorithm, FP-growth.
In this article, we learned about machine learning, why it is needed and what are its types.
Happy Learning. ☺️
