Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
Docker Platform-
Docker provides the ability to package and run an application in a loosely isolated environment called a container. The isolation and security allow you to run many containers simultaneously on a given host. Containers are lightweight and contain everything needed to run the application, so you do not need to rely on what is currently installed on the host. You can easily share containers while you work, and be sure that everyone you share with gets the same container that works in the same way.
How Docker Works-
Docker packages, provisions and runs containers. Container technology is available through the operating system: A container packages the application service or function with all of the libraries, configuration files, dependencies and other necessary parts and parameters to operate. Each container shares the services of one underlying operating system. Docker images contain all the dependencies needed to execute code inside a container, so containers that move between Docker environments with the same OS work with no changes.
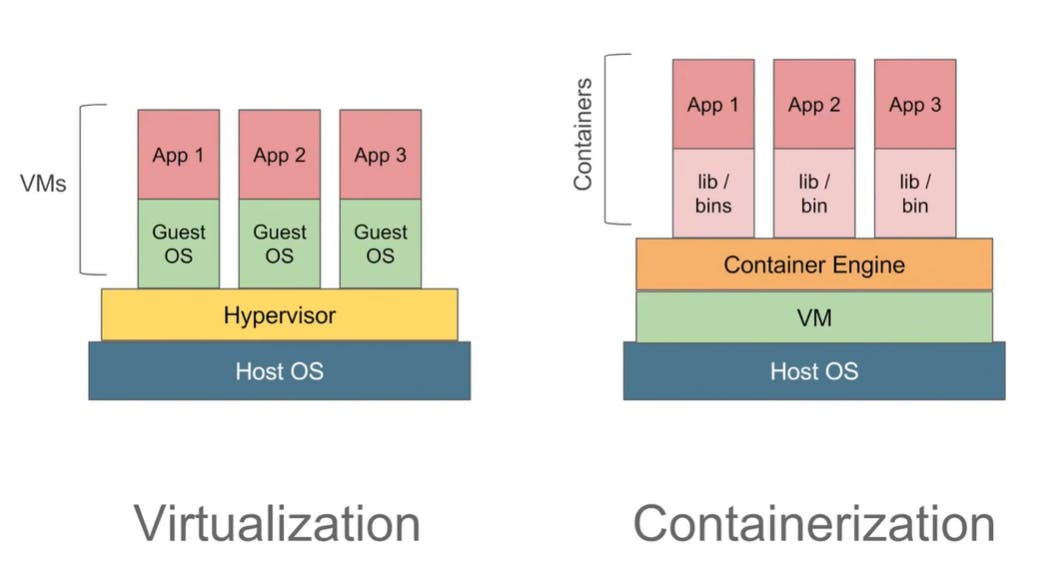
Docker uses resource isolation in the OS kernel to run multiple containers on the same OS. This is different from virtual machines (VMs), which encapsulate an entire OS with executable code on top of an abstracted layer of physical hardware resources.
Docker was created to work on the Linux platform, but has extended to offer greater support for non-Linux operating systems, including Microsoft Windows and Apple OS X. Versions of Docker for Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure are available.
Docker works via a Docker engine that is composed of two key elements: a server and a client; and the communication between the two is via REST API. The server communicates the instructions to the client. On older Windows and Mac systems, you can take advantage of the Docker Toolbox, which allows you to control the Docker engine using Compose and Kitematic.
Virtualization and containerization-
Virtualization is the technique of importing a guest operating system on top of a host operating system. This technique was a revelation at the beginning because it allowed developers to run multiple operating systems in different virtual machines all running on the same host. This eliminated the need for extra hardware resources.
Containerization is the technique of bringing virtualization to the operating system level. While virtualization brings abstraction to the hardware, containerization brings abstraction to the operating system.
Virtualization aims to run multiple OS instances on a single server, whereas containerization runs a single OS instance, with multiple user spaces to isolate processes from one another. This means containerization makes sense for one AWS cloud user that plans to run multiple processes simultaneously.
A container holds a single function for a specific task or a microservice. By splitting each individual application function into a container, microservices improve enterprise service resilience and scalability.
Benefits of Docker-
Build app only once- An application inside a container can run on any system that has docker installed. So there is no need to build and configure the app multiple times on different platforms.
More sleep and less worry- With docker, you test your application inside a container and ship it inside a container. This means the environment in which you test is identical to the one on which the app will run in production
Portability- Docker containers can run on any platform. It can run on your local system, Amazon ec2, Googe cloud platform, VirtualBox etc...
Version Control-Like Git, Docker has an in-built version control system. Docker containers work just like GIT repositories, allowing you to commit changes to your Docker images and version control.
Isolation- With Docker every application works in isolation in its own container and does not interfere with other applications on the same system.
Why Docker is used in DevOps-
Containers can be deployed from one server, allowing development teams to save time, money, and effort when deploying and testing applications. The primary reason to use containers instead of VMs for development is that they help developers use serverless applications, automating and speeding up application deployment.
The value of Docker for DevOps continues as it enables an entirely isolated application to be deployed to multiple servers. As it spreads to the servers, no other applications can access it. The only exposure of the container is to the internet and the Docker client.
Components of Docker-
Docker Engine- Docker Engine (the heart of the Docker system) is simply the docker application that is installed on your host machine. It works like a client-server application
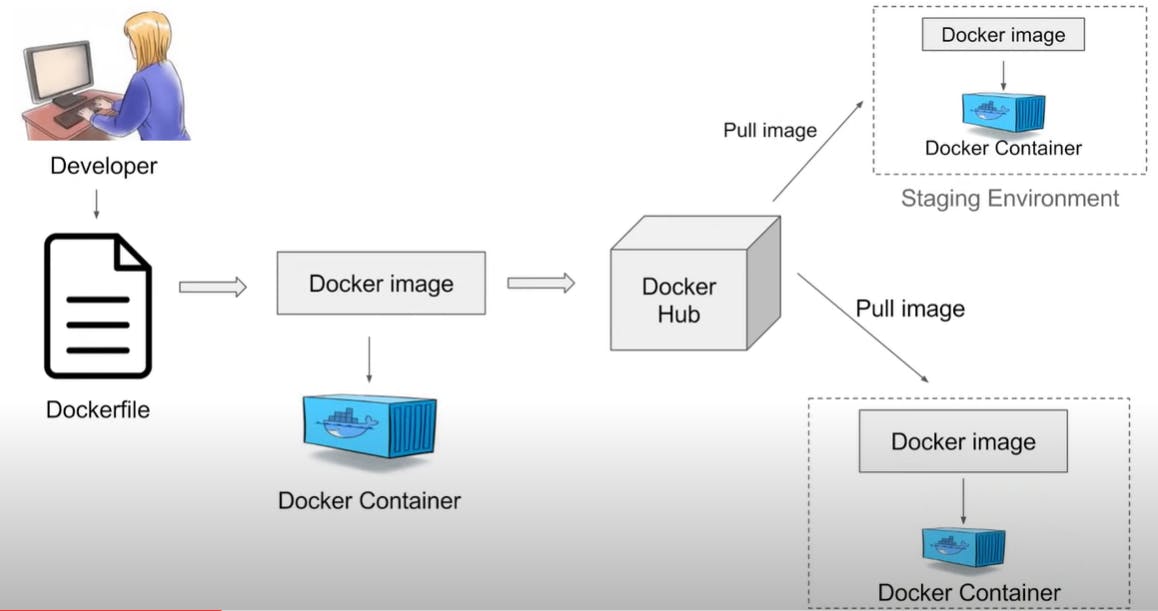
Docker Image- Docker Image can be compared to a template that is used to create Docker Containers. They are the building blocks of a Docker Container. These Docker images are created using the build command. These read-only templates are used for creating containers by using the run command.
Docker registry- Docker Registry is where the Docker Images are stored. The Registry can be either a user’s local repository or a public repository like a Docker Hub allowing multiple users to collaborate in building an application.
Docker Container- Containers are ready applications created from Docker Images or you can say a Docker Container is a running instance of a Docker Image and they hold the entire package needed to run the application.
Containers and Dockers have the potential to build innovative possibilities for several industries and enterprises.
