Jupyter Notebook is an open-source, web-based interactive environment, which allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, mathematical equations, graphics, maps, plots, visualizations, and narrative text. It integrates with many programming languages like Python, PHP, R, C#, etc. Jupyter Notebooks are a spin-off project from the IPython project, which used to have an IPython Notebook project itself. The name, Jupyter, comes from the core supported programming languages that it supports: Julia, Python, and R. Jupyter ships with the IPython kernel, which allows you to write your programs in Python, but there are currently over 100 other kernels that you can also use.
Advantages of Jupyter Notebook
There are the following advantages of Jupyter Notebook -
1. All in one place: As you know, Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web-based interactive environment that combines code, text, images, videos, mathematical equations, plots, maps, graphical user interface and widgets to a single document.
2. Easy to convert: Jupyter Notebook allows users to convert the notebooks into other formats such as HTML and PDF. It also uses online tools and nbviewer which allows you to render a publicly available notebook in the browser directly.
3. Easy to share: Jupyter Notebooks are saved in the structured text files (JSON format), which makes them easily shareable.
4. Language independent: Jupyter Notebook is platform-independent because it is represented as JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format, which is a language-independent, text-based file format. Another reason is that the notebook can be processed by any programing language, and can be converted to any file formats such as Markdown, HTML, PDF, and others.
5. Interactive code: Jupyter notebook uses ipywidgets packages, which provide many common user interfaces for exploring code and data interactivity.
Disadvantages of Jupyter Notebook
There are the following disadvantages of Jupyter Notebook:
It is very hard to test long asynchronous tasks. Less Security It runs cell out of order In Jupyter notebook, there is no IDE integration, no linting, and no code-style correction.
Installation of Jupyter Notebook using pip package To install the Jupyter Notebook, first, you need to install the Python. You can follow the below steps to download the Python.
Step1: Click on the link python.org/downloads/windows to download the latest version of the Python.
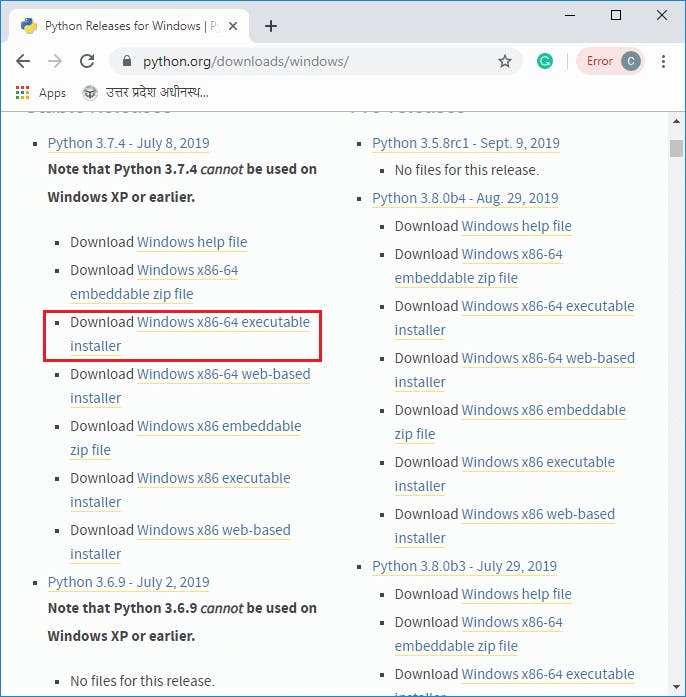
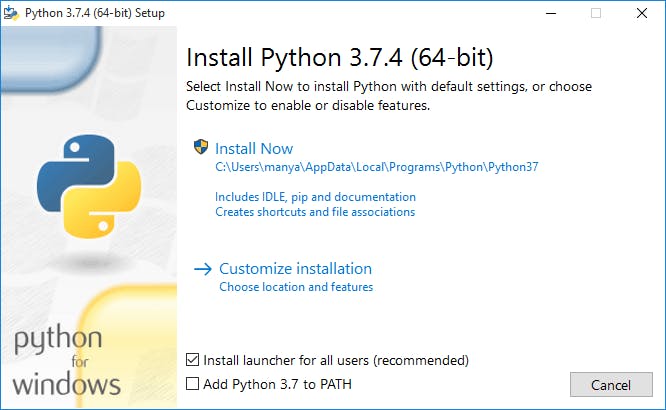
Step2: Now, double click on the downloaded file, the following window is opened. Select Install Now to Install Python.
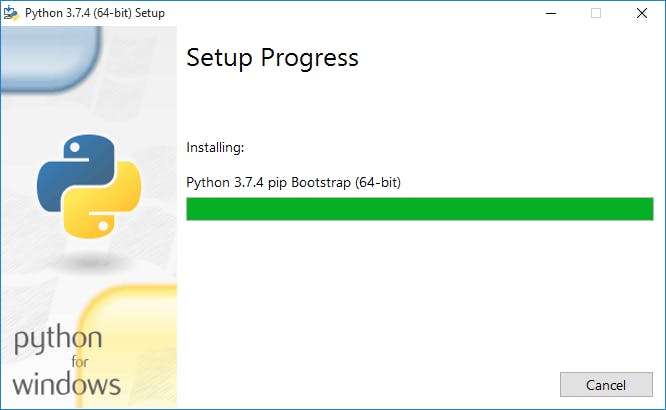
Step3: You can see that installation is in process.
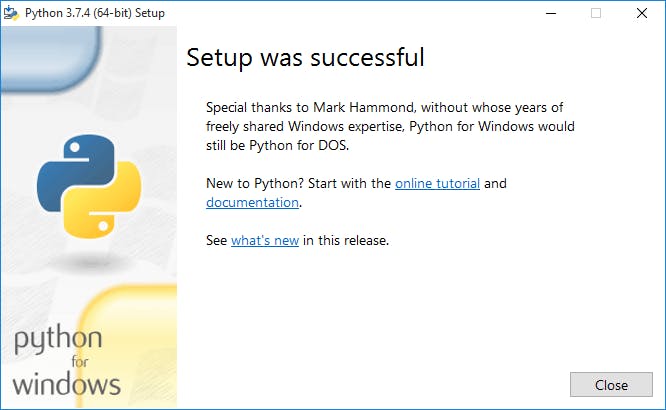
Step4: Once the installation is completed, the following window is open, you simply click on the close.
Components of Jupyter Notebook
There are the following three components of Jupyter Notebook -
1. The notebook web application: It is an interactive web application for writing and running the code. The notebook web application allows users to:
Edit code in the browser with automatic syntax highlighting and indentation. Run code on the browser. See results of computations with media representations, such as HTML, LaTex, png, pdf, etc. Create and use JavaScript widgets. Includes mathematical equations using Markdown cells.
2. Kernels: Kernels are the separate processes started by the notebook web application that is used to run a user's code in the given language and return output to the notebook web application.
In Jupyter notebook kernel is available in the following languages:
Python Julia Ruby R Scala node.js Go
3. Notebook documents: Notebook document contains a representation of all content which is visible in the notebook web application, including inputs and outputs of the computations, text, mathematical equations, graphs, and images.
4. The Cell Cell menu allows you to run one cell, a group of cells, or all the cells. You can also go here to change a cell’s type, although I personally find the toolbar to be more intuitive for that.
5. The Widgets The Widgets menu is for saving and clearing widget state. Widgets are basically JavaScript widgets that you can add to your cells to make dynamic content using Python (or another Kernel).
6. The Insert The Insert menu is just for inserting cells above or below the currently selected cell.
7. The View The View menu is useful for toggling the visibility of the header and toolbar. You can also toggle Line Numbers within cells on or off. This is also where you would go if you wanted to mess about with the cell’s toolbar.
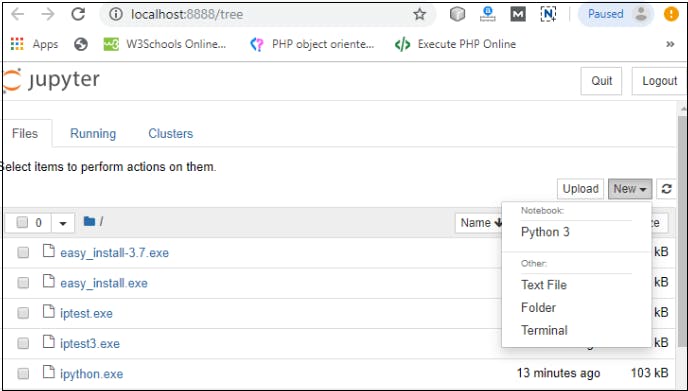
Creating a Notebook
To create a Notebook in Jupyter, go to New and select Python3.
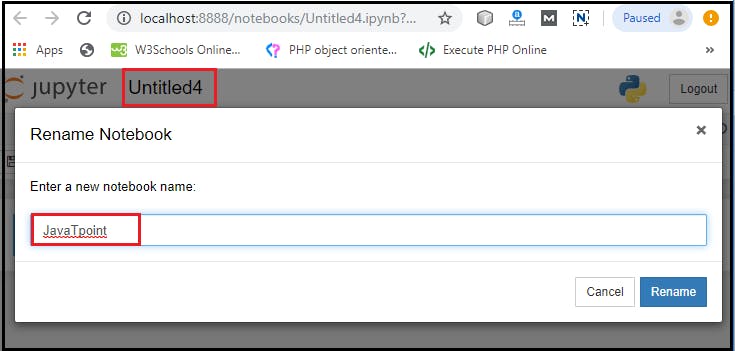
Rename the Notebook
To rename the Notebook, double click on the Untitled at the top of the screen. A pop up window will open to renaming the file. Enter a new notebook name that you want to add. Then click on the Rename.
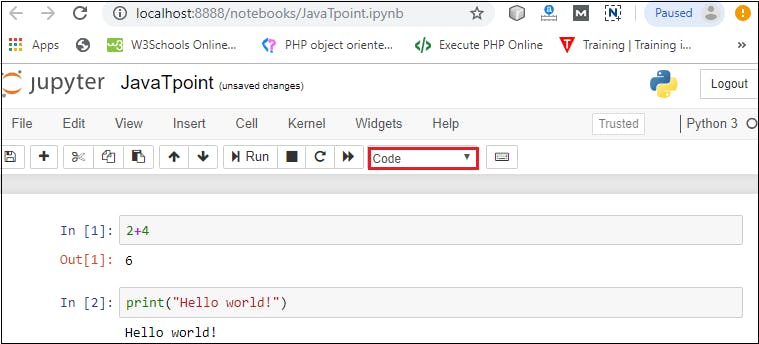
How to write and run a program in Jupyter
After renaming the file, click on the first cell in the notebook to enter in the edit mode. Now you can write the code in working area. After writing the code, you can run it by pressing the Shift+ Enter key or directly click on the run button at the top of the screen.
Types of cells in Jupyter Notebook
There are the following four types of cells used in the Jupyter Notebook.
1. Code Cell
The contents present in a code cell is treated as statements in a programming language of the current kernel. By default, Jupyter notebook's kernel is in Python so you can write Python statements in a code cell. When you run the statement, its output is displayed below the code. Output can be presented in the form of text, image, matplotlib plots, or HTML tables.
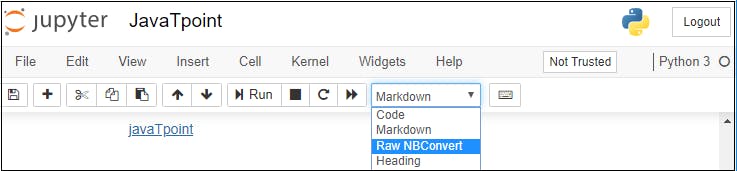
2. Markdown Cell
Markdown cell provides documentation to the notebook and makes the notebook more attractive. This cell contains all types of formatting features such as making text bold and italic, headers, displaying ordered or unordered list, Bullet lists, Hyperlinks, tabular contents, images, etc.
3. Raw NBConvert Cell
Raw NBConvert Cell provides a place where you can write output directly. These cells are not evaluated by the notebook kernel.
4. Heading Cell
The Jupyter Notebook does not support the heading cell. When you select the Heading from the drop-down menu, a pop will open on the screen which is shown in the below screenshot.
IPyWidgets in the Jupyter Notebook The ipywidgets provides many common user interfaces for exploring code and data interactively.
By default, ipywidgets are installed in Anaconda or you can also install it manually with conda.
Some example of ipywidges are given below:
- Text widget The text widget allows the user to write the String:
- Button widget The button widget is similar to the HTML button. To create button, type the following code.
from ipywidgets import widgets
button = widgets.Button(
description='Press Me', )
button
- color picker
The Color picker allows you to select a color as per to your requirement.
from ipywidgets import widgets
color_picker = widgets.ColorPicker(
concise = True,
description = 'Background color:',
value = '#efefef',
)
color_picker
