Hello everyone, welcome to this Blog .You must know the basic concept of ReactJS . If you're not, I would recommend that you go through the ReactJS documentation.
We will use the following components in this application:
- ReactJS
- Material UI
- Firebase
- ExpressJS
- Postman
Application architecture :
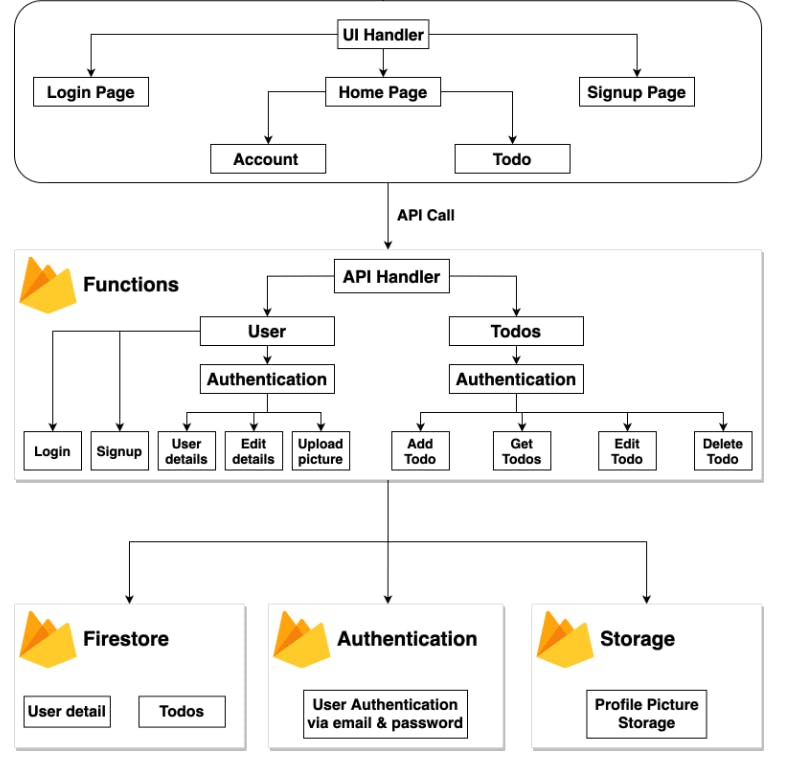
Understanding our components: Why using a firewall is critical and necessary. Furthermore, it offers a Real-time database, a Serverless component, a Storage bucket, and secure authentication. To avoid having to deal with HTTP Exceptions, we are using Express in this situation. In our functions component, we'll use all the Firebase packages. This is due to the fact that we don't want to make our client programme too large, since this tends to slow down the UI's loading time. You may find a git commit with the code created in that segment at the beginning of each section. Additionally, this repository has the whole code if you want to see it.
Developing Todo APIs In this section, we are going to develop these elements:
- Configure the firebase functions.
- Install the Express framework and build Todo APIs.
- Configuring firestore as database. The Todo API code implemented in this section can be found at this commit.
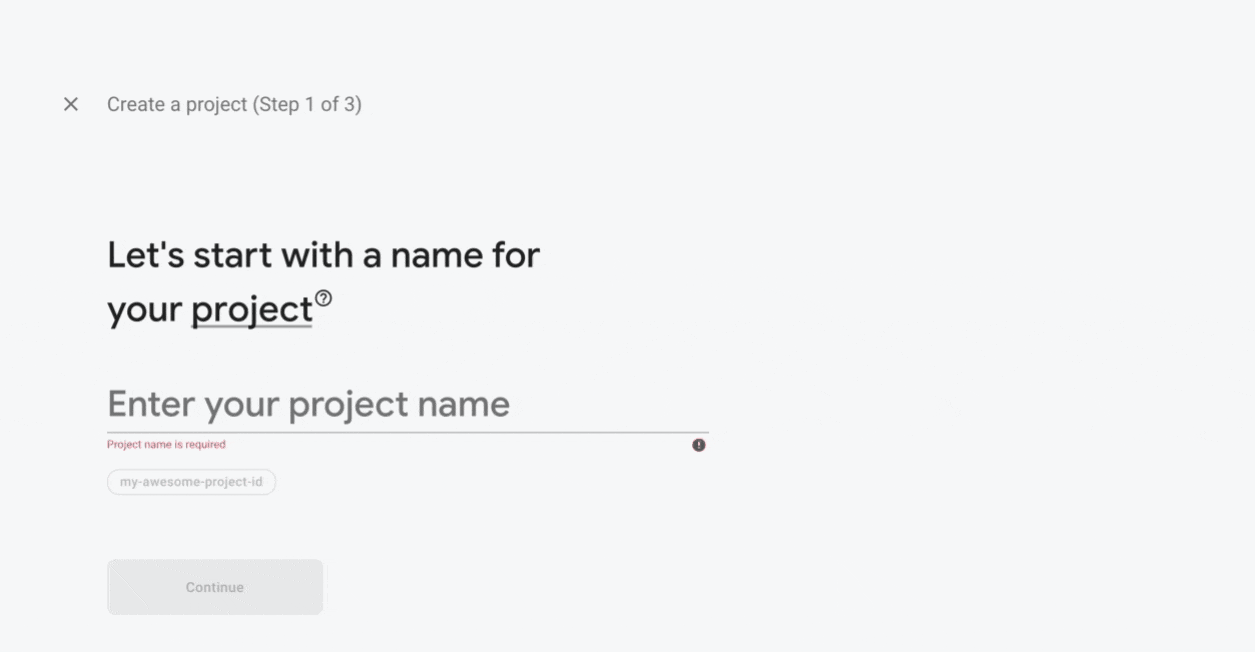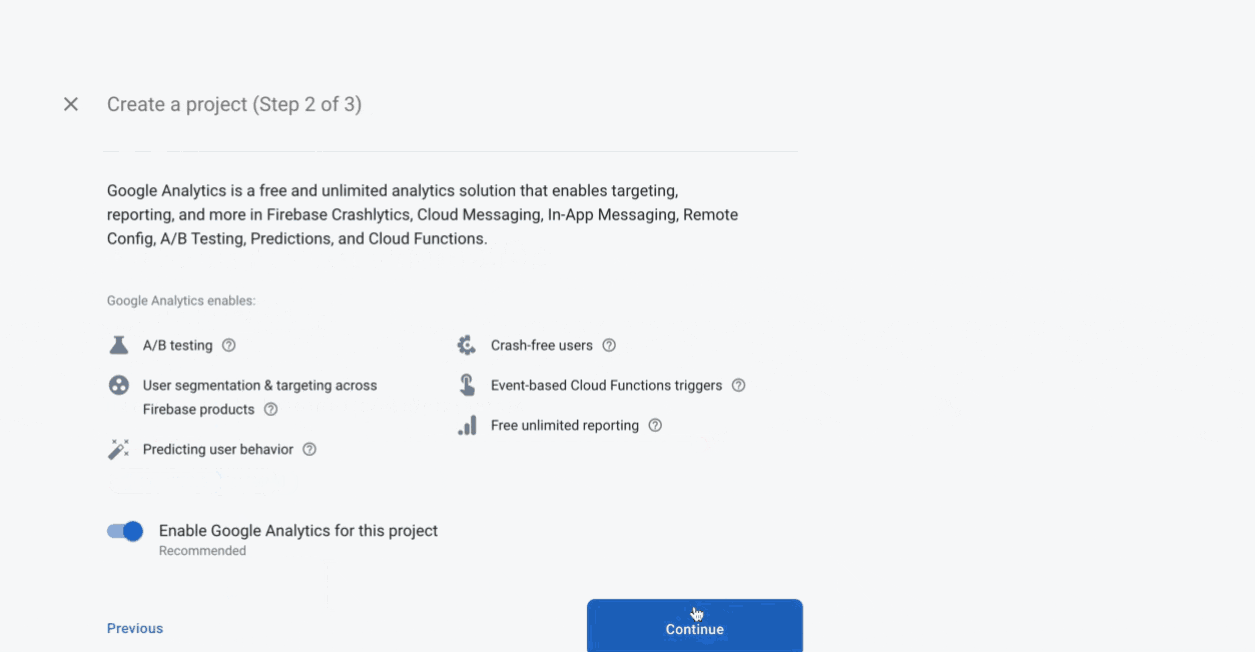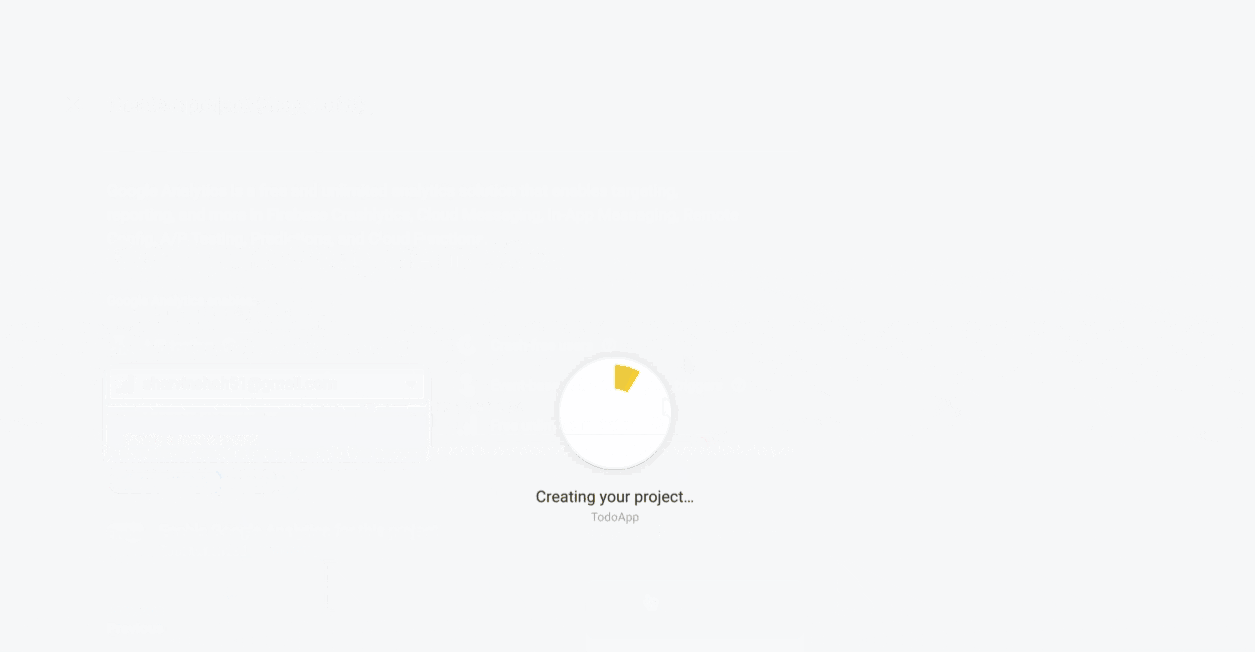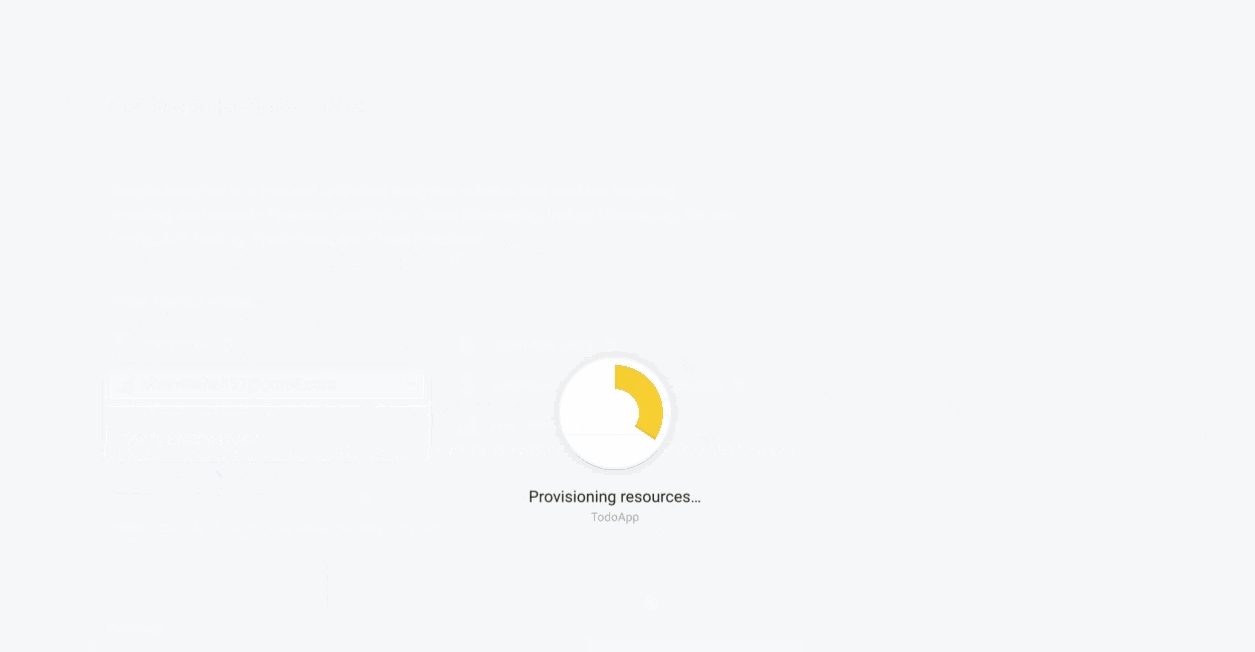
Configure Firebase Functions: Go to the Firebase console. Firslty Add your new project

Follow the gif down below step by step to configure the firebase project.
A dialogue box containing instructions on how to set up the Firebase Functions will appear. Visit your neighbourhood. Launch a command-line programme. Use the command below to install the firebase tools on your computer:
After that, use the firebase init command to set up the firebase features in your local environment. When initialising the firebase function in the local environment, choose the following options:
Which Firebase CLI features do you want to set up for this folder? Press Space to select features, then Enter to confirm your choices => Functions: Configure and deploy Cloud Functions
First, let’s associate this project directory with a Firebase project …. => Use an existing project
Select a default Firebase project for this directory => application_name
What language would you like to use to write Cloud Functions? => JavaScript
Do you want to use ESLint to catch probable bugs and enforce style? => N
Do you want to install dependencies with npm now? (Y/n) => Y
Now open the index.js under functions directory and copy-paste the following code:
const functions = require('firebase-functions');
exports.helloWorld = functions.https.onRequest((request, response) => {
response.send("Hello from Firebase!");
});
Use this command to deploy the code to Firebase functions:
firebase deploy
You will receive the following logline at the end of your command line once the deployment is complete:
Complete deployment!
Console for the project: https://console.firebase.google.com/project/todoapp-id>/overview
The API's URL may be found by going to Project Console > Functions. The URL will appear as follows:
https://<hosting-region>-todoapp-<id>.cloudfunctions.net/helloWorld
Paste this URL into your browser once you copy it. You will receive the subsequent response:
Hello ! from firebase
This demonstrates that the configuration of our Firebase function is correct.
Developing User APIs :
1. User Login API:
First, we need to install the firebase package, which consists of the Firebase Authentication library, using the following command:
npm i firebase
Once the installation is done go to the functions > APIs directory. Here we will create a users.js file. Now Inside index.js we import a loginUser method and assign the POST route to it.
2. User Sign-up API:
The default authentication mechanism of firebase only allows you to store information like email, password, etc. But we need more information to identify if this user owns that todo so that they can perform read, update and delete operations on it.
To achieve this goal we are going to create a new collection called users. Under this collection, we will store the user’s data which will be mapped to the todo based on the username. Each username will be unique for all the users on the platform.
Go to the index.js. We import a signUpUser method and assign the POST route to it.
//index.js
const {
..,
signUpUser
} = require('./APIs/users')
app.post('/signup', signUpUser);
3. Upload User Profile Picture:
Our users will be able to upload their profile picture. To achieve this we will be using Storage bucket. Go to the Firebase console > Storage and click on the Get started button.
4. Get User Details:
Here we are fetching the data of our user from the database. Go to the index.js and import the getUserDetail method and assign GET route to it.
// index.js
const {
..,
getUserDetail
} = require('./APIs/users')
app.get('/user', auth, getUserDetail);
5. Update user details:
Now let’s add the functionality to update the user details. Go to the index.js and copy-paste the following code:
// index.js
const {
..,
updateUserDetails
} = require('./APIs/users')
app.post('/user', auth, updateUserDetails);
Now go to the users.js and add the updateUserDetails module below the existing getUserDetails :
// users.js
exports.updateUserDetails = (request, response) => {
let document = db.collection('users').doc(`${request.user.username}`);
document.update(request.body)
.then(()=> {
response.json({message: 'Updated successfully'});
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
return response.status(500).json({
message: "Cannot Update the value"
});
});
}
6. Securing Todo APIs: To secure the Todo API so that only the chosen user can access it, we will make a few changes in our existing code. Firstly, we will update our index.js as follows:
// index.js
// Todos
app.get('/todos', auth, getAllTodos);
app.get('/todo/:todoId', auth, getOneTodo);
app.post('/todo',auth, postOneTodo);
app.delete('/todo/:todoId',auth, deleteTodo);
app.put('/todo/:todoId',auth, editTodo);
We have updated all the Todo routes by adding auth so that all the API calls will require a token and can only be accessed by the particular user.
**Originally published by : free code camp. Thanks Sharvin Shah for writing such informative blog.