Ensemble learning is a supervised learning technique used in machine learning to improve overall performance by combining the predictions from multiple models.
Instead of relying on a single model, ensemble learning methods use multiple models to make a prediction. Ensemble learning is based on the idea that a group of models can perform better than any single model because the individual models can complement each other's strengths and weaknesses.
Types of Ensemble Methods:
There are different types of ensemble learning methods, including:
- Voting: A Voting Classifier is a machine learning model that trains on an ensemble of numerous models and predicts an output (class) based on their highest probability of chosen class as the output. It simply aggregates the findings of each classifier passed into Voting Classifier and predicts the output class based on the highest majority of voting. The idea is instead of creating separate dedicated models and finding the accuracy for each of them, we create a single model which trains by these models and predicts output based on their combined majority of voting for each output class.
Voting Classifier supports two types of voting:
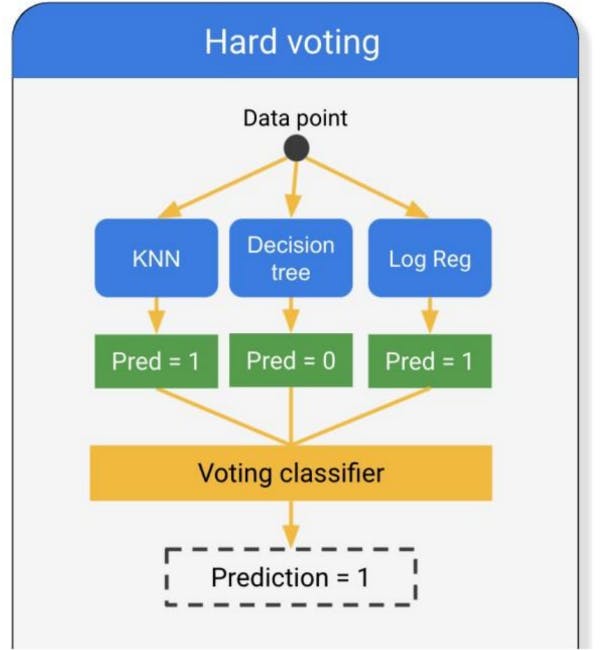
Hard Voting: In hard voting, the predicted output class is a class with the highest majority of votes i.e the class which had the highest probability of being predicted by each of the classifiers. Suppose three classifiers predicted the output class(A, A, B), so here the majority predicted A as output. Hence A will be the final prediction.
Soft Voting: In soft voting, the output class is the prediction based on the average probability given to that class. Suppose given some input to three models, the prediction probability for class A = (0.30, 0.47, 0.53) and B = (0.20, 0.32, 0.40). So the average for class A is 0.4333 and B is 0.3067, the winner is clearly class A because it had the highest probability averaged by each classifier
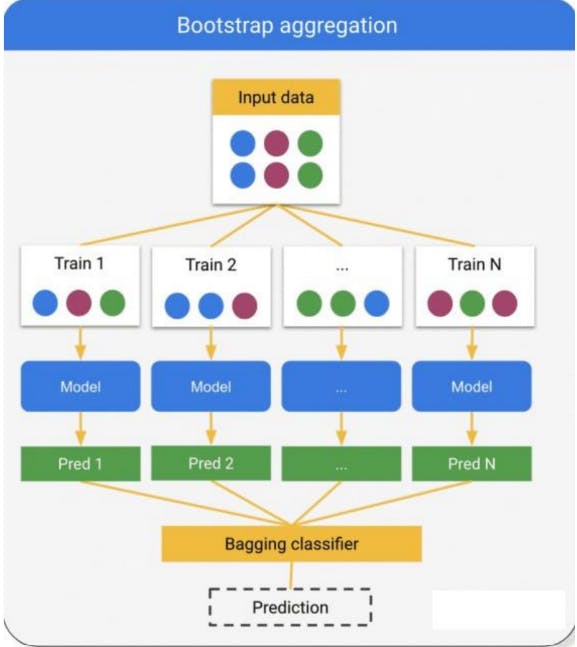
Bagging: In bagging, multiple models are trained on different subsets of the training data, and their predictions are combined using averaging or voting to make the final prediction.
Bagging, or bootstrap aggregation, is an ensemble method that reduces the variance of individual models by fitting a decision tree on different bootstrap samples of a training set.
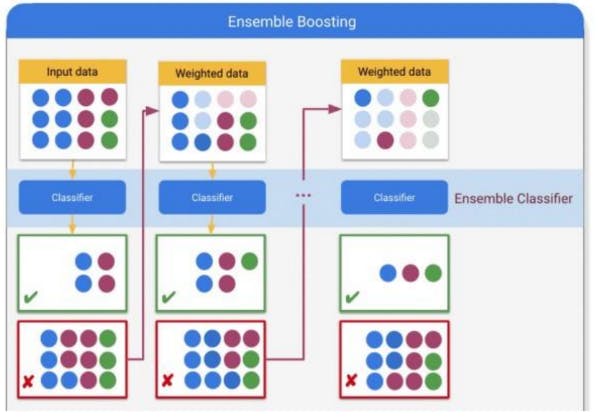
Boosting: Boosting is a method that sequentially trains models on the same dataset, with each model trying to improve on the mistakes of the previous model. The final prediction is a weighted combination of the predictions of all the models.
Boosting is an ensemble method that converts weak learners into strong learners by having each predictor fix the errors of its predecessor. Boosting can be used in classification and regression problems.
Stacking: In stacking, multiple models are trained on the same dataset, and their predictions are used as input to train a meta-model that makes the final prediction.
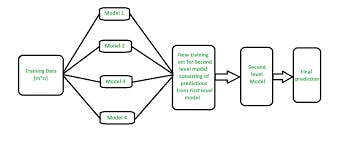
Stacking (sometimes called Stacked Generalization) is a different paradigm. The point of stacking is to explore a space of different models for the same problem. The idea is that you can attack a learning problem with different types of models which are capable to learn some part of the problem, but not the whole space of the problem. So, you can build multiple different learners and use them to build an intermediate prediction, one prediction for each learned model. Then you add a new model which learns from the intermediate predictions of the same target. This final model is said to be stacked on top of the others, hence the name. Thus, you might improve your overall performance, and often you end up with a model which is better than any individual intermediate model.
Ensemble learning has been shown to be effective in improving the accuracy and robustness of predictive models in various domains, including image classification, natural language processing, and financial forecasting.
