DevOps is a set of practices that combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to improve collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. The goal of DevOps is to enable organizations to deliver software products and services more quickly and efficiently by automating and optimizing the software development and deployment processes.
DevOps involves a cultural shift towards collaboration and communication between different software development and deployment teams. It also involves using various tools and technologies to automate and streamline the software development and deployment processes, such as continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), infrastructure as code (IaC), and monitoring and logging tools.
By implementing DevOps practices, organizations can achieve faster deployment times, higher quality software products, and improved customer satisfaction. DevOps also helps to reduce the risk of errors and downtime by enabling faster feedback loops and more frequent testing and deployment.
How does DevOps work-

DevOps works by promoting collaboration, communication, and automation between development and operations teams. Here are the key steps in how DevOps works:
Planning and Design: In this phase, development and operations teams work together to plan and design the software product or service. This includes defining requirements, designing the architecture, and selecting the appropriate technologies.
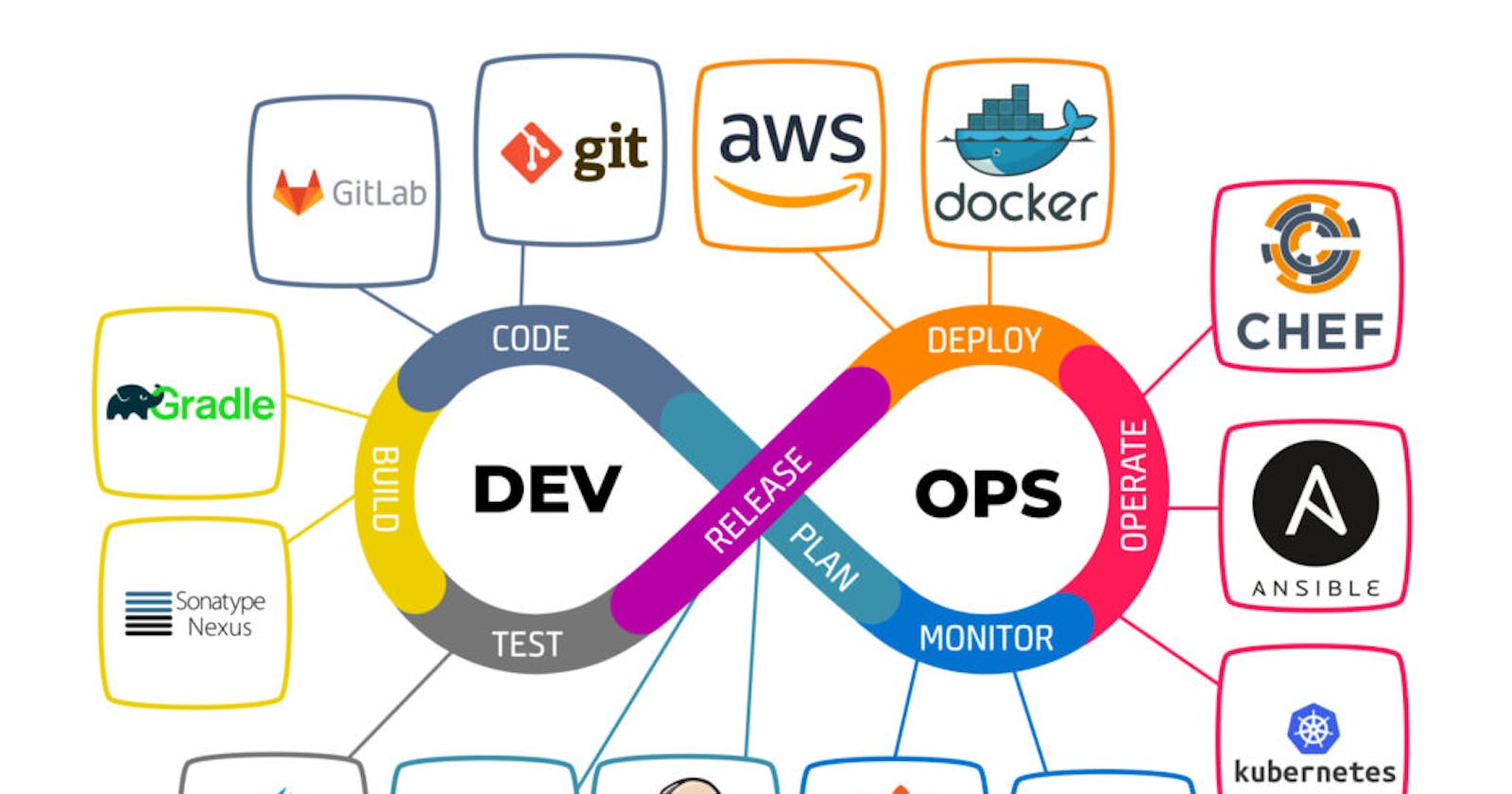
Development: In this phase, developers write the code for the software product or service. They use tools such as Git for version control and Jenkins for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD).
Testing: In this phase, developers and testers test the software product or service to ensure that it meets the requirements and works as expected. They use tools such as Selenium for automated testing and JMeter for load testing.
Deployment: In this phase, the software product or service is deployed to production. This is often done using automated deployment tools such as Ansible and Docker.
Monitoring and Maintenance: In this phase, operations teams monitor the performance and availability of the software product or service using tools such as Nagios and ELK stack. They also perform maintenance tasks such as updating software components and scaling the infrastructure.
Continuous Improvement: In this phase, teams use feedback from users and monitoring data to continuously improve the software product or service. They use tools such as Grafana for data visualization and analysis.
By following these steps and using DevOps tools and practices, teams can achieve faster deployment times, higher quality software products, and improved customer satisfaction. DevOps also helps to reduce the risk of errors and downtime by enabling faster feedback loops and more frequent testing and deployment.
Use of DevOps-
The aim of DevOps is to improve the collaboration and communication between development and operations teams and to automate and streamline the software development and deployment processes. DevOps aims to achieve the following:
Faster Delivery
Higher Quality
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Increased Efficiency
Reduced Risk
DevOps Tools-
There are a lot of DevOps tools available in the market that can be used to automate and streamline the software development and deployment processes. Here are some popular DevOps tools:
Git: Git is a version control system used for managing source code changes.
Jenkins: Jenkins is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) tool that helps automate the software development and deployment processes.
Ansible: Ansible is an open-source automation tool used for configuring and managing IT infrastructure.
Docker: Docker is a containerization tool used for creating and managing containers.
Kubernetes: Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration tool used for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Terraform: Terraform is a tool for building, changing, and versioning infrastructure safely and efficiently.
Nagios: Nagios is an open-source monitoring system used for monitoring the availability and performance of IT infrastructure.
ELK Stack: The ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) is a collection of open-source tools used for log management, monitoring, and analysis.
Grafana: Grafana is an open-source data visualization and monitoring tool used for creating and sharing real-time dashboards.
These are just a few examples of DevOps tools. There are many other tools available for different stages of the software development and deployment lifecycle, such as testing, security, and collaboration. The choice of DevOps tools depends on the specific needs of the organization and the project.

DevOps is widely adopted by companies of all sizes across various industries. Here are some examples of companies that are known for using DevOps practices:
Amazon: Amazon is known for its DevOps culture and its use of continuous deployment practices.
Netflix: Netflix has a strong DevOps culture and uses many open-source tools and technologies to automate its software development and deployment processes.
Google: Google is known for its use of containers and its emphasis on automation in its software development and deployment processes.
Microsoft: Microsoft has adopted DevOps practices to improve its software development and deployment processes and to deliver products and services more quickly and efficiently.
Etsy: Etsy, an online marketplace for handmade and vintage goods, has a strong DevOps culture and uses many open-source tools and technologies to automate its software development and deployment processes.
Salesforce: Salesforce has adopted DevOps practices to improve its software development and deployment processes and to deliver products and services more quickly and efficiently.
These are just a few examples of companies that use DevOps. In reality, DevOps has been adopted by many companies across a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, retail, and more.
In summary, the aim of DevOps is to create a culture of collaboration and communication between development and operations teams, while leveraging automation and optimization to deliver high-quality software products more quickly and efficiently.