Table of contents
The cloud has revolutionized how businesses operate, offering scalability, agility, and cost-effectiveness. However, with this evolution comes the crucial need for robust security measures. This blog will guide you through the fundamental aspects of cloud security, illustrating the flow with a comprehensive diagram for better understanding.
Understanding the Threats:
Before diving into security practices, it's essential to acknowledge the potential threats lurking in the digital landscape:
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access and exfiltration of sensitive information.
Malware Attacks: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or steal data.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Overwhelming a system with traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
Insider Threats: Malicious activities by individuals with authorized access.
Misconfigurations: Improperly configured cloud resources creating vulnerabilities.
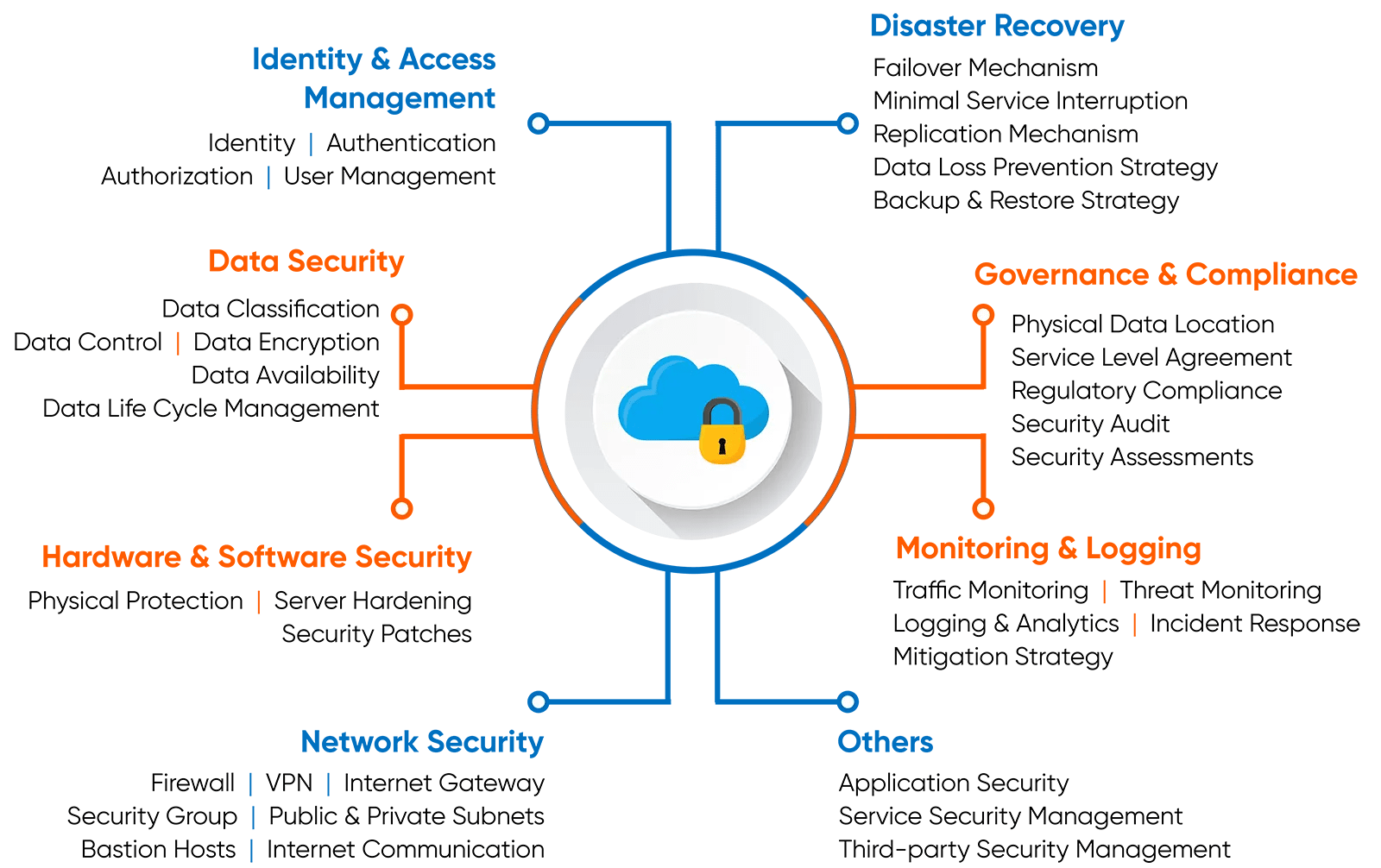
Identity and Access Management (IAM): This layer governs who and what can access cloud resources. Implementing strong authentication, authorization, and access controls is vital.
Data Security: This layer protects data at rest, in transit, and in use. Encryption, data loss prevention (DLP), and data masking are essential tools for securing sensitive information
Hardware & Software Security: The solid foundation. Secure your physical servers, virtual machines, and software with regular updates and maintenance.
Network Security: The gatekeeper. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and segmentation act as your first line of defense, controlling information flow and identifying suspicious activity.
Disaster Recovery: The backup band. Be prepared for the unexpected with data backups, recovery procedures, and a comprehensive disaster plan to ensure business continuity.
Governance & Compliance: The conductor. Clear security policies, compliance management, and employee training ensure everyone is in tune and regulations are met.
Monitoring & Logging: The watchful eyes and ears. SIEM systems and log management tools monitor activity, providing insights and identifying potential threats.
Additional Instruments:
Application Security: Fortify your apps against vulnerabilities.
Service Security Management: Secure cloud services offered by others.
Encryption: Safeguard data confidentiality across all stages..
Implementing Best Practices:
Beyond the framework, several best practices enhance cloud security:
Regular Security Assessments: Proactively identify and address vulnerabilities.
Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to ensure confidentiality.
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security beyond passwords.
Regular Backups: Ensure data recovery in case of incidents.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhere to relevant industry and regional data privacy regulations like GDPR.
Conclusion:
Cloud security is a continuous journey, not a destination. By understanding the threats, implementing a layered security framework, and adhering to best practices, you can build a robust and resilient cloud environment. Remember, security is a shared responsibility between cloud providers and users. Work closely with your cloud provider to ensure your security posture is well-defined and continuously improved.
