In today's fast-paced tech world, delivering high-quality software quickly and reliably is paramount. This is where CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment) comes in. It's a powerful set of practices that automates critical parts of the software development lifecycle, leading to:
1. Faster releases: Get your features and bug fixes to users quicker.
2. Improved quality: Catch and fix bugs earlier in the development process.
3. Reduced risk: Automate repetitive tasks to minimize human error.
4. Increased developer productivity: Free developers to focus on creating new features.
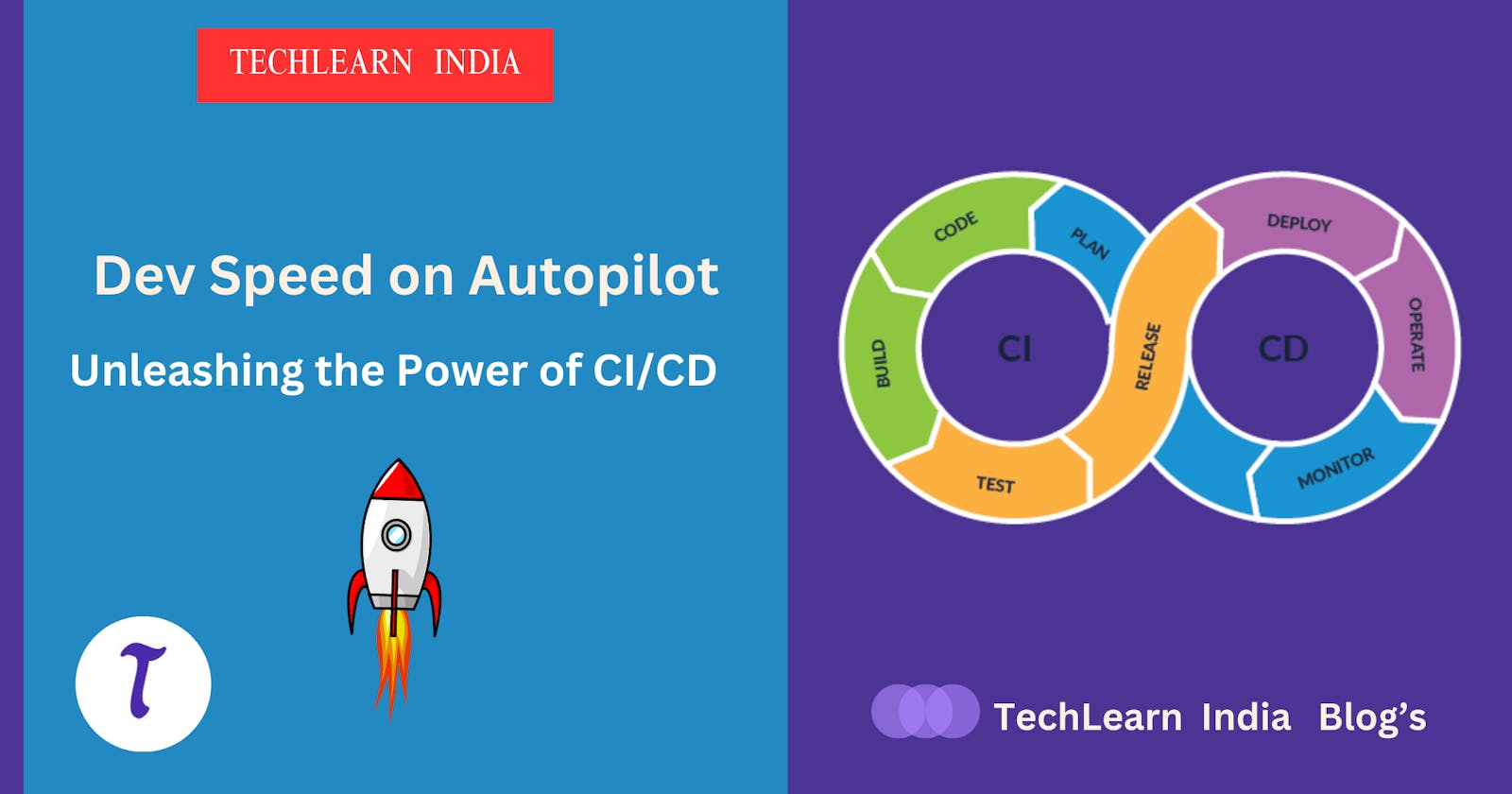
CI/CD can be visualized as a pipeline with distinct stages:
1. Continuous Integration (CI):
* Developers frequently commit their code changes to a shared central repository (e.g., Git).
* Automated builds and tests are triggered upon each commit.
* Builds ensure code compiles and runs without errors.
* Tests verify if new code introduces any bugs or breaks existing functionality.
* Early detection of issues allows for faster fixes.
- Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD):
* Once code passes all tests in CI, it's automatically packaged and deployed to a staging or production environment.
* Continuous Delivery (CD): The focus is on preparing the code for deployment (e.g., packaging, configuration management). A manual approval step might be included before deploying to production.
*Continuous Deployment (CD):Automated deployment directly to production after successful testing (assuming it meets pre-defined criteria).
Benefits of CI/CD:
* Faster Time to Market: Deliver new features and fixes to users quickly, keeping them engaged.
* Improved Software Quality: Early detection and resolution of bugs lead to more stable and reliable software.
* Reduced Costs: Automation minimizes manual effort and rework, saving time and resources.
* Increased Developer Productivity:** Developers spend less time on repetitive tasks and more time on innovation.
* Enhanced Collaboration:** Improved communication and visibility across development teams.
Several popular CI/CD tools are available, such as Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, and Travis CI. These tools integrate seamlessly with your development workflow, automating builds, tests, and deployments.
Getting Started with CI/CD using Docker: A Step-by-Step Guide
We explored the power of CI/CD in the previous section. Now, let's delve into how to implement it using **Docker**, a popular containerization technology. Docker allows you to package your application with all its dependencies into a lightweight, portable unit called a container. This ensures consistent execution environments across development, testing, and production stages.
**Step-by-Step Guide (Sample Example):**
**Scenario:** We'll build a simple Node.js application that displays a welcome message.
1. Project Setup:
* Create a project directory named `ci-cd-example`.
* Initialize a Git repository: `git init`
* Create a `package.json` file and add the following content:
{
"name": "ci-cd-example",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "A simple Node.js application",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "node index.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.18.2"
}
}
* Create an `index.js` file with the following code:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Welcome to CI/CD with Docker!');
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('Server listening on port 3000');
});
2. Create a Dockerfile:
* Create a file named `Dockerfile` with the following content:
# Use a lightweight Node.js base image
FROM node:18-alpine
# Copy package.json and package-lock.json
COPY package*.json ./
# Install dependencies
RUN npm install
# Copy the application code
COPY . .
# Expose the port
EXPOSE 3000
# Run the application
CMD [ "npm", "start" ]
Explanation:
* This `Dockerfile` defines instructions to build a Docker image.
* It starts with a lightweight Node.js base image.
* Copies `package.json` and `package-lock.json` to install dependencies.
* Copies the application code from the current directory.
* Exposes port 3000 where the application runs.
* Runs the `npm start` command to start the application.
3. Build the Docker Image:
* Open a terminal in your project directory.
* Build the Docker image using the following command:
docker build -t ci-cd-example:latest .
- CI/CD Integration (Sample with Docker Hub):
We'll use a simple example with Docker Hub, a public image registry. However, CI/CD tools like Jenkins integrate seamlessly with Docker for automated builds and deployments.
* Push the image to Docker Hub (requires a Docker Hub account):
docker login -u your_username -p your_password
docker push ci-cd-example:latest
5. Running the Application:
* You can now run the application from the built Docker image:
docker run -p 8080:3000 ci-cd-example:latest
* This command runs a container from the image, mapping port 8080 on your host machine to port 3000 within the container.
* Access the application in your browser at `localhost:8080`.
This is a very basic example. A full CI/CD pipeline would typically involve:
Setting up a CI/CD tool (e.g., Jenkins) to automate the build and deploy process on every code commit.
* Creating different environments (development, testing, production) using Docker Compose or Kubernetes.
TechLearn India: Your Gateway to CI/CD Mastery
Whether you're a beginner or looking to enhance your CI/CD expertise, TechLearn India offers a variety of courses. Learn from industry professionals and gain practical knowledge to implement CI/CD pipelines effectively in your projects.
Embrace CI/CD and empower your development team to deliver high-quality software faster and more efficiently!
#CICD #SoftwareDevelopment #DevOps #Automation #TechLearnIndia**