INTRODUCTION: In order to have as few implementation dependencies as feasible, Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language. Because it is a general-purpose programming language ; compiled Java code can run on any platforms that accept Java without the need to recompile. This is known as writing once, running anywhere (WORA). Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture
As of 2019, Java was one of the most popular programming languages in use according to GitHub,particularly for client–server web applications, with a reported 9 million developers.
Did You know ?
Original name for Java was OAK, it was because of the oak tree which grew up in front of developers windows. It was conveniently changed into Java.
NOTEWORTHY QUALITIES : The popularity of the language can be attributed to Java's several noteworthy qualities, including:
- Versatility : Java has long been the standard programming language for building software development tools like Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, and NetBeans IDE, as well as Web and Android applications.
- Tools for development : Undoubtedly one of Java's most exciting aspects is the Integrated Development Environment (IDE). The Java IDE is a set of editors, debuggers, and automation tools.
- User-friendliness :Java has an English-like syntax that makes it perfect for beginners. Java may be studied in two phases: core Java and advanced Java.
- Exemplary documentation : Java is totally free because it is an open-source programming language. An essential aspect of Java is its thorough documentation. It comes with a comprehensive handbook that explains any problems you could run across when programming in Java.
- Strong API : The Application Programming Interface (API) of Java is broad and thorough, with a variety of methods that may be used directly in any code, despite the fact that it only includes roughly fifty keywords.
- A huge neighbourhood: One factor contributing to Java's success is the support it receives from the community. It has the distinction of being the second-largest Stack Overflow community.
What is the purpose of Java? Java proficiency is clearly a well-liked and sought-after ability. But what does Java programming serve? We briefly discussed a few Java use cases before; we go into more detail on these and additional Java examples further down. Java has a wide range of applications:
- gaming consoles : Game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine use programming languages like C# and C++ when it comes to game production. Java, on the other hand, is a fantastic option if you want to learn how to design games and visuals from scratch. There are several libraries and frameworks available, including LibGDX.
- Web-based programmes : Java is a well-known server-side programming language that is often used for constructing web applications. Spring, Struts, Hibernate, Apache Hadoop, and JSF are among of the most popular Java frameworks for constructing Web applications. Java is also used by famous websites such as LinkedIn, AliExpress, Amazon, and many others.
- Big data : Aside from Python, which is used in Big Data, there are many other popular programming languages. Even so, when it comes to Big Data Technology, most programmers prefer Java. The reason for this is that most famous Big Data tools, such as Hadoop and Deeplearning4j, use Java and its community support is excellent when it comes to Big Data Technology.
- Android apps :Java is the official programming language for Android development, with Java accounting for 46.2 percent of all Android applications. It’s used by Android Studio, which is the official IDE for developing Android apps. So, if you are familiar with the Java programming language, Android development will be considerably easier for you.
SYNTAX :
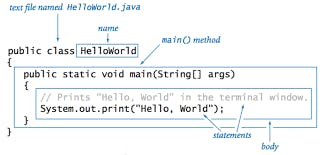
About Java programs, it is very important to keep in mind the following points.
Case Sensitivity − Java is case sensitive, which means identifier Hello and hello would have different meaning in Java.
Class Names− For all class names the first letter should be in Upper Case. If several words are used to form a name of the class, each inner word's first letter should be in Upper Case.
Example: class MyFirstJavaClass
Method Names− All method names should start with a Lower Case letter. If several words are used to form the name of the method, then each inner word's first letter should be in Upper Case.
Example: public void myMethodName()
Program File Name − Name of the program file should exactly match the class name.
When saving the file, you should save it using the class name (Remember Java is case sensitive) and append '.java' to the end of the name (if the file name and the class name do not match, your program will not compile).
Identifiers in Java:
Identifiers are the basic building blocks of a Java program. We use identifiers to give names to the different parts of the program such as variables, objects, classes, methods, arrays, etc. The rules for naming identifiers in Java are:
- Identifiers can contain alphabets, digits, and underscore(_) and dollar($) sign characters.
- They must not be a reserved word or keyword in Java, like true, false, while, etc.
- Identifiers must not begin with digits
- Identifiers can be of any length
- Java is case sensitive, so uppercase and lowercase identifiers are treated differently.
Keywords in Java:
Keywords are the reserved words in Java that convey a different meaning to the compiler. We cannot use the keywords as normal identifier names but only for a special purpose. In Java, there are 51 keywords. Some of the keywords in Java are: abstract, boolean, byte, char, long, short, int, finally, extends, implements, interface, package, new, while, for, do, break, continue, return, public, private, this, case, final, default, etc.
Literals in Java :
A literal in Java refers to the constants or the data items that have fixed values. There are different types of Literals in Java. They are Numeric, Floating, character, strings, boolean, null. They are also divided further into subcategories. Let’s discuss them separately:
a. Numeric Literals Numeric literals represent numbers. There are 4 types of numeric literals in Java:
(i). Integer Literals: Integer literals are the whole numbers without fractional part and they are the number of base 10. For example, 34, 76, 9896, etc.
(ii). Binary Literals: Binary literals are the number with base 2. For example, 0101, 0011, 011, etc.
(iii). Octal Literals: Octal literals are the numbers with base 8. They must not contain 8 and 9. For example, 77, 565, 450, etc.
(iv). Hexadecimal Literals: Hexadecimal literals are the numbers with base 16. They can contain the digits from 0 to 9 and alphabets from A to F. For Example, AC87, 1F7B, 24D6, etc.
b. Floating-point Literals
We can call floating-point literals as real literals. The floating-point literal specifies the numeric values only with the use of a fractional point(.). They can be a fractional form or exponential form. For Example, 10.876, 152.4E07, -15.6, etc.
c. Character Literals in Java
The character-literals deal with characters enclosed in single-quote. They can contain only a single character within single quotes ‘ ’. They are of following types:
i. Single quoted character: The single-quoted character encloses all the uni-length characters within single quotes. Example- ‘z’,’j’, ‘A’, etc.
ii. Escape Sequences: These are the characters that come after backslash and perform a specific function when printed on the screen such as a tab, creating a new line, etc. Example: ’\n’, ‘\b’, ‘\t’, etc.
Conclusion: Java projects provide strict compile-time error checking typically associated with Pascal, allowing instructors to introduce students to GUI programming, networks, threads, and other important concepts used in modern software. . Overall, the Java project provides a complete design for the extension language.
